Lupine Publishers Journal of Surgery and Journal of Case Studies: Currently case studies drag the concentration of the investigators since each case present provides deep understanding in diagnosis and treatment methods. It is devoted to publishing case series and case reports. Articles must be genuine
Wednesday, July 31, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Nanotechnology in Concrete: Sm...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Nanotechnology in Concrete: Sm...: Lupine Publishers | Journal of Civil Engineering Research Abstract Concrete changes the world. Nanotechnology changes...
Tuesday, July 30, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers: The Biodiversity of Aquatic Gas...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers: The Biodiversity of Aquatic Gas...: Lupine Publishers: The Biodiversity of Aquatic Gastropods in the Step... : Earth and Environment journals | Lupine Publishers Abstract...
Lupine Publishers: Interior Environmental Design, Heal? | Lupine Publ...
Lupine Publishers: Interior Environmental Design, Heal? | Lupine Publ...: Open Access Journal of Complementary & Alternative Medicine | lupine Publishers Abstract Osteoporosis is a largely p...
Monday, July 22, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Advances in Robotics & Mechani...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | Advances in Robotics & Mechani...: Journal of Robotics & Mechanical Engineering | Lupine Publishers Smart Robotics for Smart Healthcare Abstract The...
Lupine Publishers| Neurosarcoidosis: A Review of the State of Art
Lupine Publishers| Medical Care Research and Review
Abstract
Keywords: Sarcoidosis; Neurosarcoidosis; Central Nervous System Diseases; Peripheral Nervous System Diseases
Introduction
Neurosarcoidosis
The involvement of the central and peripheral nervous system (neurosarcoidosis) is rare, clinically happening in about 5-10% of patients with sarcoidosis, with an average age of onset around 33-41 years [1]. Because of the rarity of this entity and the nonspecificity of its clinical and radiological findings, there is surely a high percentage of poorly diagnosed cases, mainly in an initial approach, as the neurological involvement can be found in up to 25% of autopsies from patients with sarcoidosis [1,2]. Non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, headache, cognitive dysfunction and mood disorders are frequent in cerebral neurosarcoidosis, but the clinical picture is usually dominated by cranial neuropathy or aseptic basilar meningitis. The damage of the optic nerve, the most frequently affected followed by the facial nerve, is associated with a poor prognosis in terms of visual recovery [3]. Spinal neurosarcoidosis can be divided into intramedullary and extramedullary involvement (leptomeningeal, extradural, vertebral and disc involvement); paresthesia and weakness of the lower extremities are the main symptoms, although it often presents as symmetric sensory motor polyneuropathy. Rarely, cases of sudden paraplegia can occur, along with bowel and bladder dysfunction [3].Diagnosis
The Zajicek criteria are the mostly adopted classification system for neurosarcoidosis established in 1999 and later revised. The other set of criteria belong to WASOG (World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders), updated in 2014. The specificity and sensitivity of these two options are unknown [4]. A definite diagnosis of neurosarcoidosis can only be established with a positive biopsy of the affected nervous system, frequently considered impossible or too invasive; for this reason, the biopsy is usually performed outside the central nervous system, in a peripheral nerve or another affected and more accessible organ (as neurosarcoidosis frequently coexists with other organ involvement). None of the serum biomarkers used nowadays have been accepted as the one that stablishes the diagnosis, including the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) or the serum soluble activity of the interleukin-2 receptor (sIL2 receptor) [1].Levels of ACE in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) have a low sensitivity (between 24-55%), but may raise the suspicion of neurosarcoidosis due to its high specificity (around 94%). It seems that there is no correlation between serum and CSF levels of ACE and serum levels do not correlate with the degree of clinical activity [5]. Image findings should not be considered alone for the diagnosis of neurosarcoidosis, but always included in an appropriate diagnostic algorithm. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred imaging technique because it provides the best definition for brain and spinal cord disease [3,4]. Meningeal involvement can appear as nodular or diffuse enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1- weighted images, mainly in the basilar meninges, as opposed to intraparenchymal lesions that manifest as multiple small, nonenhancing periventricular or subcortical white matter lesions, with high signal on T2-weighted images [3]. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) can reveal areas of hypermetabolism that correspond to active lesions in asymptomatic sites, which can be used to identify suitable sites to do a biopsy, although there is a lack of evidence regarding the use of FDG-PET and its usefulness in neurosarcoidosis [4]. Histopathologically, neurosarcoidosis is characterized by the presence of noncaseating epithelioid granulomas, the same lesions as those found elsewhere in the body in systemic disease. These granulomas although not specific for sarcoidosis, are valuable diagnostic clues [1]. The differential diagnosis includes: tuberculosis, especially in endemic areas, other infections like histoplasmosis, aspergillosis and cryptococcosis, but also granulomatosis with polyangiitis [6].
Treatment
There are no international guidelines to treat neurosarcoidosis and randomized clinical trials are lacking to make treatment recommendations. Taking this into consideration, there is a general consensus that corticosteroids should be the first line of treatment, as the majority of patients improve with only glucocorticoids [1,3,7]. If the symptoms are severe, with involvement of the central nervous system, a short course of intravenous steroids is usually given, up to 1g of methylprednisolone a day for 3-5 days. Subsequently, or if the clinical symptoms are less severe, oral steroids can be administered (e.g. prednisone 40-80mg, around 1mg/kg/day), with gradually descending pattern until the lowest effective or maintenance dose (around 10mg/day). Relapse often occurs after the dose of glucocorticoids is tapered down; if the required maintenance dose is more than 10 mg a day, or if clinical response is insufficient, it is recommended to add a steroid-sparing immunomodulatory agent. The evidence is in favor of methotrexate (between 10-25mg once a week), but other immunosuppressant drugs can be considered, such as azathioprine (at 2mg/kg/day, maximum 200mg/day) [1,3,7]. In severe resistant or refractory cases, cyclophosphamide is classically used (500-1000mg iv every 2-4 weeks, or at a dose of 0.5g/m2 of body surface area every 4 weeks).Anti- TNF-alpha agents are becoming strongly recommended because of the increasing evidence of rapid reversal of clinical and radiologic features with these agents, especially infliximab (intravenously at a dose of 3-5mg/kg at weeks 0,2 and 6, with intervals of 4-6 weeks thereafter); some groups are already considering this treatment option before cyclophosphamide [3,7]. Patients treated with long-term infliximab could develop anti-infliximab antibodies that will lead to treatment failure. To avoid this, concomitant methotrexate is recommended, as an immunomodulatory agent. When to stop the treatment remains controversial [7]. Surgery is generally limited to the diagnostic biopsy rather than to the therapeutic use. Cranial mass lesions could benefit from radiation therapy, although this is not recommended as standard treatment [3].
Prognosis
There is no cure, but optimal immunosuppressive therapy can achieve clinical remission in approximately two thirds of cases, along with variable improvement in imaging findings. Despite the use of new therapies, close to one third of patients remain stable, deteriorate or die [3,8].Conclusion
For more Lupine Publishers Open
Access Journals Please visit our website:
https://lupinepublishersgroup.com/
https://lupinepublishersgroup.com/
To Know More About Open Access Publishers Please Click
on Lupine Publishers
Thursday, July 18, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Surfactant Mediated Biodegradation of Aromatic Hyd...
Lupine Publishers: Surfactant Mediated Biodegradation of Aromatic Hyd...: Journal of Oceanography | Lupine Publishers Abstract Aromatic hydrocarbons (toluene and xylene) are highly water soluble and their...
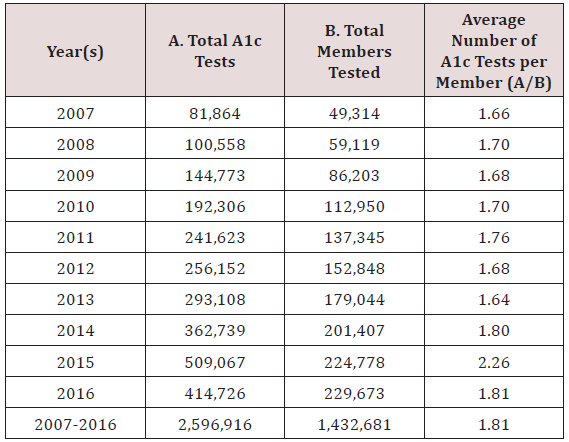
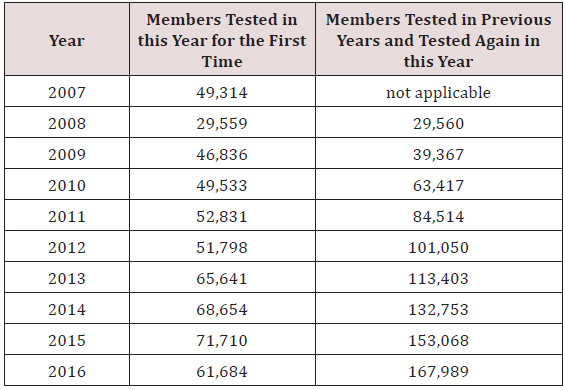
Increased A1c Testing among Members of A Large Coordinated Care Organization in Southern California- Lupine Publishers
Medical Care Research and Review- Lupine Publishers
Abstract
Keywords: A1C test; Diabetes; Prediabetes; Population health
Introduction
Blood glucose measurements are integral to the diagnosis of diabetes, its management and more recently identification of prediabetes. Prediabetes is a high risk state for developing diabetes, where blood glucose is elevated above normal levels but not yet high enough to be considered diabetes. In the case of the A1C test, categories include< 5.7% (normal), 5.7%-6.4% (prediabetes) and ≥ 6.5% (diabetes) [3]. The A1C test is used by diabetic patients and their physicians to monitor blood glucose. Regular measurement of A1C levels enables patients with diabetes and their physicians to know whether patients are reaching their A1C goals in order to minimize the adverse health outcomes associated with uncontrolled diabetes. The A1C test has the advantage of requiring no preparation and it is not sensitive to the time of day, unlike other blood glucose tests. Consequently, many providers are hopeful that the ease of the A1C test will decrease the number of undiagnosed diabetics as well as allow for identification of patients with prediabetes and therefore earlier intervention and prevention of diabetes [6].
Case Study Site, Study Goals and Results
Discussion
To Read More Click on Below Link
https://lupinepublishers.com/research-and-reviews-journal/fulltext/increased-a1c-testing-among-members-of-a-large-coordinated-care-organization-in-southern-california.ID.000125.php
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Publishers Please Visit our Website
https://lupinepublishersgroup.com/
For More Medical Care Research and Review Articles click on below link
https://lupinepublishers.com/research-and-reviews-journal/
To Know more about Open Access Publishers please click on Lupine Publishers
Wednesday, July 17, 2019
Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Nesseria Gonorrhoea at the Genitourinary Medicine Clinic, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia- Lupine Publishers
Medical Care Research and Review- Lupine Publishers
Abstract
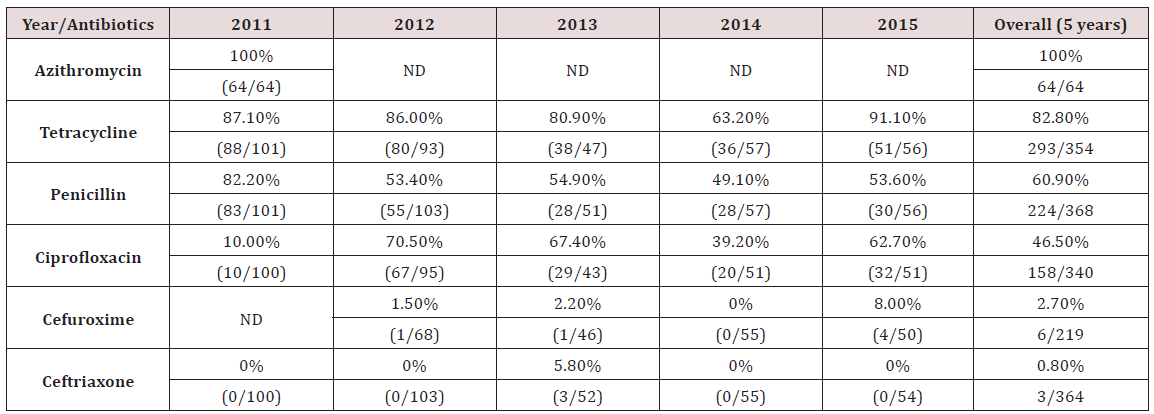
Methodology: This is a retrospective study on the antibiotic resistance patterns based on 370 culture positive gonorrhoea obtained from urethral swab samples sent between 2011 and 2015. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing by standard disc diffusion method was performed to detect sensitivity to penicillin, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, cefuroxime, azithromycin and ceftriaxone. All data was obtained from microbiology report and patient records.
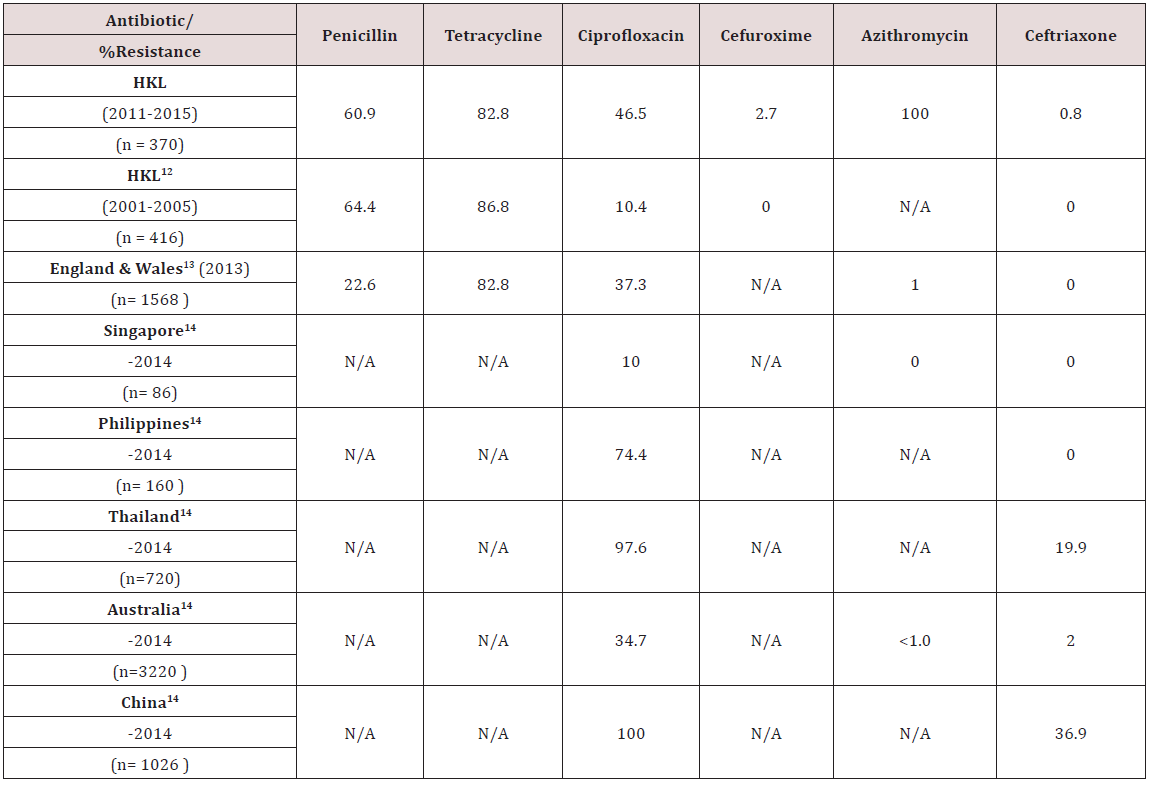
Results: A total of 370 positive culture isolates of N.gonorrhoeae (new and recurrent cases) from 2011 to 2015 were reviewed. Highest level of resistance detected was to azithromycin (100%, 64/64) followed by tetracycline (82.8%, 293/354). Resistance to penicillin was noted in 60.9% (224/368) of all isolates. Both penicillin and tetracycline showed a decreasing resistance trend from 2011-2015. The fourth commonest antibiotic resistance was to ciprofloxacin at 46.5% (158/340). Cephalosporins tested were cefuroxime and ceftriaxone, which showed resistance rates of 2.7% (6/219) and 0.8% (3/364), respectively.
Conclusion: The complete resistance to azithromycin is alarming since it is a common antibiotic used to treat urethral discharge using the syndromic approach. Penicillin and tetracycline resistance remain high in Malaysia and other Western Pacific countries. The current first line antibiotic for treating gonorrhoea in GUM Clinic, HKL is ceftriaxone. Clinicians should be aware of the newly discovered increase in resistance observed to ceftriaxone.
Keywords: Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Gonorrhoea; Antibiotic Resistance
Introduction
Unfortunately, it is also asymptomatic in more than half of women [4]. In men, untreated urethral infection can lead to epididymitis, reduced fertility, and cause urethral strictures. In women, if present, symptoms are non specific and include abnormal vaginal discharge, dysuria, lower abdominal discomfort, and dyspareunia. The lack of discernible symptoms results in unrecognized and untreated infections, which can lead to serious complications [5]. Overall, 10%-20% of female patients develop pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and, consequently, are at risk for infertility [6]. Pregnancy complications associated with gonorrhea include chorioamnionitis, premature rupture of membranes, preterm birth, ectopic pregnancies, and spontaneous abortions [5,7,8]. Infants of mothers with gonococcal infection can be infected at delivery, resulting in neonatal conjunctivitis (ophthalmia neonatorum). Such untreated conjunctivitis may lead to scarring and blindness.
Extragenital infections are common in both sexes and frequently occur in the absence of urogenital infection [9,10]. Rectal infections are usually asymptomatic but can manifest as rectal and anal pain or discharge. Pharyngeal infections are mostly asymptomatic, but mild sore throat and pharyngitis may occur. Although bacterial concentrations are generally lower than in other infection sites, the pharynx is thought to be a favourable site for resistance emergence due to acquisition of resistance traits from commensal Neisseria spp [11]. Disseminated gonococcal infections with gonococcal arthritis also occur. Because they are frequently asymptomatic, extragenital infections often remain untreated, despite their key role in disease transmission. Co-infection with other major Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) HIV, Herpes simplex virus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma genitalium, and Treponema pallidum are common and may result in synergistic effects on transmission and disease severity. Attempts to treat and control gonorrhoea are compromised by the emergence and spread of antibiotic resistant N.gonorrhoeae. Antibiotic resistance pattern vary between different geographical areas. It is therefore important to know the local antibiotic resistance pattern, so that appropriate treatment can be instituted. In Malaysia, Kanamycin was used as the first line antibiotic to treat gonorrhoea during the early 1970’s and 80’s, which was subsequently changed to Spectinomycin, followed by Ceftriaxone since the early 1990’s [12] There are many surveillance programmes on antibiotic resistance patterns of N.gonorrhoeae such as GRASP (Gonococcal Resistance to Antimicrobial Surveilance Programme), that is based in London, UK, and WHO (World Health Organization) Antimicrobial Surveilance Programme [13,14].
Materials and Methods
Results
Discussion
Azithromycin
The rate of resistance to Azithromycin in this study was higher than expected. All 64 samples tested for sensitivity to Azithromycin showed resistance. In Singapore, no resistance to Azithromycin has been documented [14]. Similarly in England & Wales and Australia, the rate of resistance is significantly lower, at 1% or less [13,14] (Table 3). Studies have indicated concerns for increasing resistance to Azithromycin, likely due to delay in diagnosis of gonorrhoea and suboptimal dose of Azithromycin used [15].Tetracycline
The rate of resistance to Tetracycline is high. In our study, 82.8% of N.gonorrhoea isolates were resistant to Tetracycline. This is slightly lower, compared to an earlier analysis done in HKL from 2001-2005, where 86.8% of isolates were resistant [12]. The resistance rates in England & Wales was similar to ours [13] (Table 3). Looking at the trend, there was a reduction in resistance rates from 87.1% in 2011 to 63.2% in 2014. However, the rate increased to 91.1% in 2015 (Table 2). In HKL, Doxycycline is sometimes used to treat non-gonoccocal urethritis but never as primary treatment for gonorrhoea. Tetracycline has never been used for treating gonorrhoea in HKL as the resistance is very high. Nevertheless, the resistance pattern is continuously monitored for epidemiological purposes.Penicillin
Since the 1940’s, Penicillin was successfully used to treat gonorrhoea, but quickly developed decreased sensitivity and deemed not a suitable treatment after 1970. This can be due to Penicillinase Producing N.gonorrhoeae (PPNG) or Chromosomal Mediated Resistance N.gonorrhoeae (CMRNG) [16]. Our study shows that the rate of N.gonorrhoeae resistance to Penicillin has reduced, from 82.2% in 2011 to 53.6% in 2015 (Table 2). Compared to an earlier study done in HKL in 2001-2005, there was a slight drop in resistance to penicillin in HKL from 64.4% to 60.9% in 2011-2015. However, our resistance rates were much higher compared to the resistance rate reported in England & Wales of 22.6% (Table 3) [13].Ciprofloxacin
In the early 1990’s, Ciprofloxacin was widely used especially by general practitioners to treat gonorrhoea although studies had already began demonstrating the beginning of reduced sensitivity to quinolones. The resistance to Ciprofloxacin in HKL showed a steady increase from 10.0% in 2011 to 62.7% in 2015 (Table 2). When compared to an earlier review in HKL from the period 2001- 2005, we can see marked increase in resistance to Ciprofloxacin from 10.4% to 46.5% in 2011-2015 (Table 3). The resistance rate reported in HKL from 2011-2015 was similar to England & Wales and Australia, which reported resistance of 37.3% and 34.7% respectively (Table 3) [13,14]. Among the Asian countries, Singapore reported the lowest resistance to Ciprofloxacin (10.0%) [14]. Other Asian countries, like the Phillipines, Thailand and China reported an alarmingly high resistance to Ciprofloxacin, which is between 74.4%-100% (Table 3) [14].Cephalosporin–Cefuroxime and Ceftriaxone
Although Cefuroxime is not a recommended treatment for gonorrhoea, its resistance pattern is monitored for epidemiological purposes. Our study showed a resistance rate of 2.7% to Cefuroxime in 2011-2015, whereas an earlier study in 2001-2005 showed no resistance to Cefuroxime (Table 3). Susceptibility testing for Ceftriaxone use in the treatment of gonorrhoea in HKL between 2001-2005 indicated no resistance, however, recent data from 2011-2015 showed a resistance rate of 0.8% (Table 3). Ceftriaxone is the first line treatment of gonorrhoea in HKL and clinicians should be aware that we are seeing a small percentage of resistance in some cases. No resistance was noted in Singapore and the Phillipines (Table 3) [14]. Resistance rates to Ceftriaxone in Thailand and China are significantly higher, at 19.9% and 36.9% respectively (Table 3) [14].Conclusion
To Read More Click on Below Link
https://lupinepublishers.com/research-and-reviews-journal/fulltext/antibiotic-resistance-pattern-of-nesseria-gonorrhoea-at-the-genitourinary-medicine-clinic-hospital-kuala-lumpur-malaysia.ID.000124.php
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Publishers Please Visit our Website
https://lupinepublishersgroup.com/
For More Medical Care Research and Review Articles click on below link
https://lupinepublishers.com/research-and-reviews-journal/
To Know more about Open Access Publishers please click on Lupine Publishers
Tuesday, July 16, 2019
Intracardiac Papillary Fibroelastoma: A Case Report- Lupine Publishers
Medical Care Research and Review- Lupine Publishers
Abstract
Keywords: Cardiac tumors; papillary fibroelastomas; Embolism; Echocardiography
Introduction
Case Background
Discussion
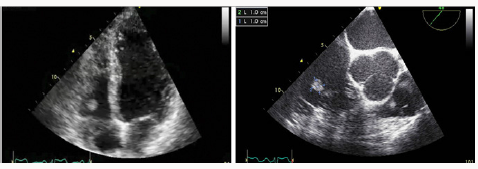
Regarding the findings in echocardiography, the lesions are usually located in the aortic valve, followed by the mitral valve, with a size between 2 and 40 mm, making them easier to detect in transesophageal echocardiograms. The overall mass is unique, with a short pedicle; it moves independently and it is attached to an endocardium surface. Given that the tumor has papillary extensions attached to the central pedicle, an image in the shape of a sea anemone is observed. Sometimes it is difficult to differentiate the lesion when it is attached to the valves when they are moving and when they are smaller than 2 mm [5,8]. Although the papillary fibroelastoma can be seen in the Computerized Axial Tomography and the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, the echocardiogram is still the best image to evaluate these lesions since they are highly mobile and can be better seen in high resolution mode or zoom mode. Larger lesions may be accompanied by calcifications, which makes it easier to identify them [1,5]. The differential imaging diagnoses of this type of tumors include Lambal’s excrescences, which look more linear and are smaller, the vegetations that are usually accompanied by valve incompetence and destruction of the valve leaflets, thrombi and valve degenerative changes. Although these tumors are formed in the heart valves, the dysfunction of these structures is rare [5,8,10]. Treatment of benign primary tumors such as papillary fibroelastoma is surgical. Some authors suggest that, in the case of tumors on the left side, they should be resected in patients without high surgical risk if the size is greater than 1 cm or during another type of heart surgery. In the case of lesions on right side of the heart, they should only be resected if they are large or moving, and if they are associated with a hemodynamically significant obstruction or with a high risk of embolism due to short circuit from right to left [5,14]. Although a significant percentage of patients are asymptomatic, we suggest that those that meet the aforementioned criteria be resected, given the high risk of cerebrovascular events and death, aiming to use a technique that conserves the native valve [1,15]. If the patient does not have any symptoms or if the tumor is small, has no pedicle and is not moving, of if it is not possible to perform the surgical procedure due high surgical risk or due to the patient’s preference, we suggest antiplatelet therapy, even though there are few publications that support this recommendation [5,15].
Conclusion
Ethical Responsibilities
a. Data Confidentiality: The authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data. Right to privacy and informed consent. The authors declare that patient data does not appear in this paper.
To Read More Please Click on below link
For more Medical Care Research and Review articles Please Click Here:
To Know More About Open Access Publishers Please Click on Lupine Publishers
Monday, July 15, 2019
Expectations in the Purchase of Health Insurance Plans: An Experiment in the City Of Barranquilla (Colombia)_ Lupine Publishers
Medical Care Research and Review- Lupine Publishers
Abstract
Introduction
However, this way of relating the interaction between health insurance policies and policy holders does not reflect the role of subjectivity and its influence on people´s decision to purchase health insurances. In order to contrast the perspective of McCue and Hall, a survey was conducted to 50 medical insurance policyholders in the city of Barranquilla (Colombia) on the perception of various services offered by their insurance policies before being used following the experiment of Chew-Graham (2017) that highlights the possibility of having complementary medical insurance as a determinant for a high perception of quality before use it. The respondents were divided into two groups, the first group of 25 insured has additional benefits in their health insurance (spas, hydrotherapy, thalassotheraphy) while the other group of 25 does not. From a Likert survey ranging from 1 to 5, they were asked about three items: a variety of doctors and health centers that their insurance plan offer, medical attention and follow-up care after medical procedures, timely assistance before, during and after consumption of medical services.
It should be taken into account that none of the policyholders in the two groups had used their insurance policies until the date of the survey, which, according to McCue and Hall’s position, the surveys should show no perception of quality of their insurance plans before use it. The hypothesis of this experiment is that policyholders have different expectations in their medical insurance before using them because they have variable preferences (Gritcher and Cox, 1996) where policyholders are encouraged in different ways to select different health insurance that does not necessarily reflect a completely rational decision. In this sense, direct and indirect incentives [4] influence the creation of biases that influence the choice of policyholders, hence the creation of different expectations before the acquisition and consumption of medical insurance services.
Methodology and conceptual framework
Hypothesis
The hypothesis is that the perception of quality of complementary medical insurance is no necessarily related to its consumption in a different cultural and geographical context. This is based on a Likert survey with three items with scale from 1 to 3 where 1 is a low perception and 3 a high. The first item asks about whether the insurance policy contracted offers a wide variety of medical centers and specialist doctors for their health care services. The second item asks about whether the insurance company continually assists its policyholders after a medical procedure. The third item asks about whether the insurance company provides timely assistance in the face of an adverse health condition. The first step of the study was the selection and verification of the suitability of the respondents in terms of having complementary medical insurance subscribed in the same period of time. Half (25) with complementary medical care benefits services and the other 25 without it, with similar policies in the availability of specialist doctors and health centers. In this step, insurers that had similarity in their policies with differences in complementary services were also selected. The second step was to carry out the survey of the target population based on the three items described above. The third step was the statistical analysis by means of the tests Test Kolmogorov Smirnov (KS) and Test U Mann Whitney in order to determine if the provision of complementary medical services affects the perception of quality of medical insurance even when these are not consumed.Main objective
The main objective is to statistically determine the perception of quality of 50 insured surveyed in the city of Barranquilla with complementary medical insurance replying the Chew- Graham experiment in order to determine if the perception of quality varies for the two groups before they use their insurance benefits. The study population was divided into two groups; the first group 25 insured have the option to enjoy wellness medicine procedures (thalassotherapy, hydrotherapy and spas) with a lower co-payment than the individual payment of procedures. The second group of 25 is composed of policyholders who do not have this additional benefit even when both policies are very similar in coverage of medicines, clinics and number of physicians to which the insured can access. The sample was obtained on December 6, 2017, first group of policyholders’ states that they have not yet enjoyed the extra benefits of their policies.Participants
Two groups of 50 individuals with complementary medical insurance in the city of Barranquilla were surveyed. The first group of 25 insured has a health insurance policy that offers coverage in complementary medical services (thalassotherapy, spa, and spa) and the other 25 insured do not have that additional benefit. Both groups of respondents have similar characteristics in gender parity (25 men and 25 women), education (both groups claimed to have a university degree), age (35-45 years) and per capita income (they claimed to have between 5-10 minimum legal monthly salary). The insurers that offer the two different medical insurance are are Colmedica Prepaid Medicine and Coomeva Prepaid Medicine. Both providers of complementary medical insurance.This study was divided in three phases. In the first one, a characterization diagnosis of the participants was made in order to determine if they have similarity in levels of education, income, gender parity and ages. In the second stage, the target population was asked to complete a three-item survey on their perception of the quality of the two insurance policies in the city of Barranquilla. In the third phase it was determined if there is a differentiated perception about the quality of the health services through the Kolmogorov Smirnov Test (K-S) and the U Mann Whitney Test.
Parametric and non-parametric tests
Before the beginning of the statistical tests to prove the hypothesis, it is necessary to highlight an important element as a fundamental requirement to choose an appropriate statistical test. In this case, the difference between parametric and nonparametric tests will be briefly mentioned, in order to justify the usefulness of the U Mann Whitney test. Parametric statistics refers to the set of statistical procedures that allow knowing the distribution of the data, that is, if the data meet the necessary parameters to know what type of distribution the data has. On the contrary, if the distribution of the data is unknown and it is not known how these behave, then non-parametric tests should be applied. In addition, it is convenient to use non-parametric tests when minimum requirements or statistical assumptions are not met, such as small sample sizes (n <30), non-normal data distribution, that is, when there is a tendency in the data and its distribution is not in the form of a Gaussian bell and the variables are not continuous [5]. To apply parametric tests it is necessary to verify that the requirements or assumptions that conform to this type of tests are met.i. Test Kolmogorov Smirnov (K-S)
a. P-value> 0.05 → The data comes from a normal distribution, it is possible to use the parametric techniques.
b. P-value <0.05 → The data have an unknown distribution, it is advisable to use nonparametric techniques.
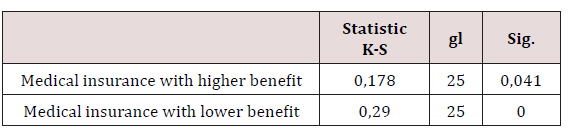
For the research case, this procedure was applied in order to determine the normality of the data, finding the following: As seen in table 1, the results show a p-value <0.05 for each group evaluated, that is, the data have an unknown distribution and do not meet the assumption of normality, therefore, it is acceptable to use non-parametric techniques for achieving the main objective.
Source: Own calculation with SPSS, 23.
U Mann Whitney test
The U Mann Whitney test is a type of non-parametric technique in which the purpose is to contrast the mean of a variable in two independent groups and verify whether it is different or not in a significant way. The U Mann Whitney test is the non-parametric alternative to the Student T test, when it is not possible to comply with the assumptions or requirements to apply it. This test is used when the observations of both groups are independent and the variables are ordinal or continuous (Scale from 1 to 3, ordinal), in addition, it is important to have the same size in both groups (in this case 25 surveyed in each group).Procedure
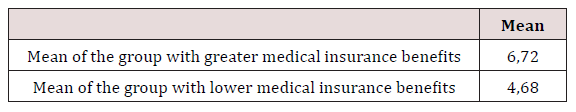
The perception of quality is composed of three variables: variety of services, support and timely medical assistance. However, to obtain a variable that would allow to include the general perception and also to compare both groups, the three questions evaluated were aggregated in order to achieve a total score for each respondent, where the highest total scores indicate a greater perception and On the other hand, lower total scores indicate a lower perception of quality. Given that the instrument consists of three questions, the highest possible score that both groups can obtain is 9 points, corresponding to answer High (3) in all. On the contrary, the minimum possible score that can be obtained by both groups is 3, corresponding to Low (1) in all the questions. In this way, the total score can be seen where the values close to the theoretical maximum (9) correspond to a better evaluation and the total scores close to the theoretical minimum (3) correspond to a low evaluation.Once the total score of each respondent was obtained, the total average per group was obtained, as shown in table 2. It is observed that in the group with greater benefits, the perception of quality in general is higher than in the group with the lowest benefits. However, it is necessary to test whether this difference is statistically significant with the U Mann Whitney test.
Source: Own calculation with SPSS, 23.
Application and interpretation of U Mann Whitney test.
The U Mann Whitney test contrasts the hypothesis if the means of both groups are the same or on the contrary they do not present differences. In this case it can be expressed as follows:a. P-value> 0.05 → The mean in both groups are the same.
b. P-value <0.05 → The mean in both groups are different.
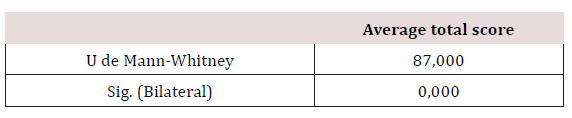
The results shown by the statistical software allow to obviate all the manual procedure of calculation of the test and to obtain the necessary values for the statistical interpretation. Table 3 allows to evaluate if the average scores (perception) between both groups are the same or not (Table 3).
Group variable: Affiliation to medical insurance policy
Discussion and Conclusion
To
Read More Please Click on below link
For
more Medical Care Research and Review articles Please Click Here:
To
Know More About Open Access
Publishers Please Click on Lupine
Publishers
Tuesday, July 9, 2019
Medical Care Research and Review- Lupine Publishers
New methods of preservation of the ovarianreserve during operations on the ovary, Individualtactics. A simple solution (preliminary report) by VG Zhegulovych in Research and Reviews on Healthcare: Open Access Journal (RRHOAJ)- Lupine Publishers
Currently, surgical treatment of the ovaries is carried out
mainly by laparoscopic entry. Surgical interventions are always
associated with the need for hemostasis. All types of energy that
are used in surgery (mechanical, electrical, thermal, welding,
laser, etc.), depending on various pathophysiological mechanisms,
affect the ovarian tissue and damage the ovarian reserve in
women of reproductive age [1,2]. The ovarian suture causes an
intense inflammatory reaction to the foreign body (tissue necrosis,
granulation tissue) even around the suture material that dissolves
within 30-60 days. In surgery, conservative hemostasis methods
involving temporary compression are widely used: hemostasis
during acute gastroduodenal ulcer bleeding, liver damage.Thus, temporary compression hemostasis can be suggested as
an alternative to thermal and ultrasound methods and as the one
that causes minimal damage to the ovarian reserve. Furthermore,
phylogenetically the ovary “got used” to permanent monthly
hemorrhages, hematomas and ischemia during ovulation. Taking
into account the peculiarities of ovarian blood supply, as well as
natural monthly traumatization of the ovaries accompanied by
the formation of hematomas in the area of an ovulation stigma, it
was decided to use temporary compression of the ovarian tissue
to achieve hemostasis [3,4].
For more information click on below link
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Journals Please visit our website:
For more Medical Care Research and Review articles Please Click Here:
To Know More About Open Access Publishers Please Click on Lupine Publishers
Monday, July 8, 2019
Medical Care Research and Review- Lupine Publishers
Efficacy of SBT (spiritualistic behavior therapy)much more fruitful than CBT (cognitive behaviortherapy) and DBT (dialectical behavior therapy)among deliberate self harm individuals by Mohammed Shafiqul Kabir in Research and Reviews on Healthcare: Open Access Journal (RRHOAJ)- Lupine Publishers
The frequently use of DBT & CBT during DSH has approximately
doubled during the last decade. However, little is known about
their efficacy for eradicating dependency on various Substances
and concerns have been raised about the potential association with
DSH (Deliberate Self Harm) and the maladaptive behaviours among
SIPD (Substance Induced Psychotic Disorder). To detect the maladaptive behaviors overall the
Substance Induced Psychotic Disorder (SIPD) patients with the risk
of DSH (Deliberate Self Harm) & suicidal attempts (Para suicide).
Efficiency of SBT (Spiritualistic Behaviour Therapy) in comparison
with DBT & CBT especially who are exposed with DSH & comorbid
substance for a prolong period.
For more information click on below link
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Journals Please visit our website:
For more Medical Care Research and Review articles Please Click Here:
To Know More About Open Access Publishers Please Click on Lupine Publishers
Wednesday, July 3, 2019
Lupine Publishers: Journal of Veterinary Science- Lupine Publishers
Lupine Publishers: Journal of Veterinary Science- Lupine Publishers: Report of Outbreak of Ruminal Impaction Due to Indigestible Foreign Bodies in Sheep, in Northwest of Iran by Mohammad Reza Mohebbi in C...
Tuesday, July 2, 2019
Medical Care Research and Review- Lupine Publishers
Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Margarida Silva Fonseca in Research and Reviews on Healthcare: Open Access Journal (RRHOAJ)- Lupine Publishers
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is the result of persistent Gastroesophageal reflux associated with symptoms and/or
complications. It is the most prevalent esophageal pathology in pediatric population and it is one of the most common causes for
medical consultations. The identification of extra esophageal manifestations and associated alarm signals allows an appropriate
treatment, an early identification of esophageal mucosal injury and prevention of complications. Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) occurs when there is incompetence of
sphincter of the Gastroesophageal junction or when raised intragastric
or intra-abdominal pressures exist sufficient to overcome this
mechanism. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) results from a
persistent GER and gives rise to troublesome symptoms or complications.
For more information click on below link
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Journals Please visit our website:
For more Medical Care Research and Review articles Please Click Here:
To Know More About Open Access Publishers Please Click on Lupine Publishers
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers| A Standard Pediatric Dental Clinic
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers| A Standard Pediatric Dental Clinic : Lupine Publishers| Journal of Dentistry and Oral Health Care Aft...
-
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers| A Standard Pediatric Dental Clinic : Lupine Publishers| Journal of Dentistry and Oral Health Care Aft...
-
Lupine Publishers | Journal of Health Research and Reviews Abstract Metabolism is the process your body uses to make energy f...
-
Lupine Publishers | Journal of Health Research and Reviews bstract Purity of the person is guarantee of his health. Spiritual and...