Abstract
Most of primary cardiac masses correspond to benign tumors within
which are the myxomas, rhabdomyomas and papillary
fibroelastomas that occupy the third place in prevalence. These lesions
are rare and are usually found incidentally in routine studies.
More than 90% of papillary fibroelastomas occur in the heart valves, the
most frequent being the aortic valve and the mitral valve.
Echocardiography studies have reported a size between 2 and 40mm, mostly
corresponding to single lesions, with a short pedicle,
which present independent movement and are attached to an endocardial
surface. The treatment is surgical since they can present
complications like embolism to the pulmonary or systemic circulation,
significant hemodynamic obstruction and death secondary
to these embolic events. We present the case of an asymptomatic patient
in whom a papillary fibroelastoma located in the tricuspid
valve was documented, which was successfully resected.
Keywords: Cardiac tumors; papillary fibroelastomas; Embolism; Echocardiography
Introduction
Heart tumors include a wide number of lesions that may be
of neoplastic or non neoplastic origin. Primary benign lesions
are approximately 90% of primary heart tumors, including
myxomas, rhabdomyomas, fibroids, and lipomas, among others
[1]. Metastatic lesions are more frequent than primary lesions,
found in nearly 18% of stage IV cancer [2]. Most heart tumors
are incidentally found during routine cardiac imaging, and their
prevalence in autopsy series is less than 0.1% [3-5]. Patients with
primary tumors are usually asymptomatic until lesions grow
large and generate symptoms related to mechanical obstruction,
valve interference, alterations in contractility or in the electrical
conduction system, generating arrhythmias and blockages [1,6].
Papillary fibroelastoma is the third most prevalent primary tumor
after myxoma and rhabdomyoma. It may compromise valve surface,
although cases of compromised interventricular or interatrial
septum have also been reported [6,7]. Next we present the case
of an asymptomatic patient with papillary fibroelastoma in the
tricuspid valve, which was successfully resected.
Case Background
51-year-old man with a history of controlled hypertension and
an active smoker, asymptomatic from a cardiovascular point of view
who underwent a transthoracic echocardiogram during his routine
checkup in his hometown. The exam revealed a mass attached to
the tricuspid valve, and thus the patient was referred to our hospital
for assessment. He was hemodynamically stable when he checked
in at Hospital Militar Central (HMC), with no abnormal findings
after physical examination and with normal range of laboratories
and preoperative electrocardiogram values. After checking in at the
HMC, the patient underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram
to better characterize the lesion, which revealed a 11mm x 11
mm rounded, pedunculated mass of endocardial density in the
lateral valve (Figure 1), without regurgitation and with preserved
ejection fraction of the left ventricle (63%). The remainder of the
description of this study was normal. Both the transthoracic and
the transesophageal projection show a 11mm x 11 mm rounded,
pedunculated mass of endocardial density in the anterior tricuspid
valve. The subject underwent additional presurgical testing in the
form of a coronary angiography, which revealed epicardial arteries
without angiographically significant lesions. The patient’s case was
submitted to the Board of Cardiology and to the cardiovascular
surgery service, and it was concluded that he was suitable for
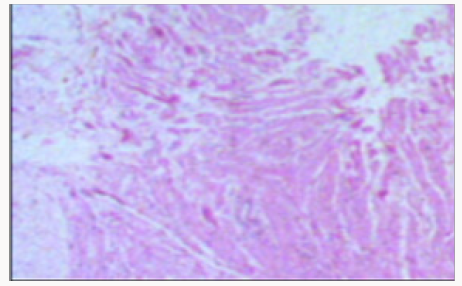
surgery. The histopathological study of the sample taken in surgery
was reported as papillary fibroelastoma type myxoid tissue mass
of mesenchymal origin with a low degree of malignancy (Figure
2). The patient evolved without complications during the postoperative
period and was discharged after 7 days of hospitalization.
Figure 1: Transthoracic (left) and transesophageal (right)
echocardiogram.
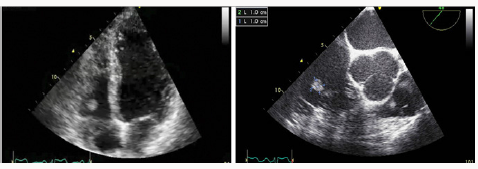
Figure 2: Sample of resected mass.
Discussion
Heart tumors or masses are rare lesions that are documented
parenthetically when performing a routine cardiac imaging. They
can be classified into neoplastic and non-neoplastic tumors, the
former being 20 to 50 times more frequent than primary tumors
[1,7,8]. The prevalence of primary tumors is very low, being between
0.001 and 0.03% according to reports in autopsy series; as for
neoplastic cardiac lesions, they can be found in about 18% of stage
IV cancer patients [2-5]. Most primary heart tumors are benign,
myxomas being the most frequent in adults, while rhabdomyoma
is the most common in children. The third most frequent primary
heart tumor in adults is the papillary fibroelastoma, which can
be generated on any surface of the endocardium, being more
commonly located in the heart valves. It makes up less than 10%
of all cardiac tumors and is the most common valve tumor [5,8,9].
Papillary fibromyosarcomas are benign proliferations consisting
of soft fibroblasts and variable collagenized stroma derived from
the endocardium. They can occur at any age, but are more common
in adults between 70 and 80 years. Over 90% of fibroelastomas
occur in the heart valves, and close to 10% happen in non-valvular
surfaces, such as the interventricular or interatrial septum
[1,8]. From a clinical point of view, up to a third of patients are
asymptomatic, so their diagnosis is mainly incidental in autopsies,
in echocardiographic studies or during a cardiovascular surgery
[10-12]. In the case of patients with symptoms, they are secondary
to obstructive effects of the coronary ostium or to embolic events
in pulmonary or systemic circulation due to detachment of mass
fragments or accumulated thrombi that have also been described
in cases of sudden death by embolization in coronary arteries and
in cases of ischemic cerebrovascular events [1,8,13].
Regarding the findings in echocardiography, the lesions are
usually located in the aortic valve, followed by the mitral valve,
with a size between 2 and 40 mm, making them easier to detect
in transesophageal echocardiograms. The overall mass is unique,
with a short pedicle; it moves independently and it is attached
to an endocardium surface. Given that the tumor has papillary
extensions attached to the central pedicle, an image in the shape of
a sea anemone is observed. Sometimes it is difficult to differentiate
the lesion when it is attached to the valves when they are moving
and when they are smaller than 2 mm [5,8]. Although the papillary
fibroelastoma can be seen in the Computerized Axial Tomography
and the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, the echocardiogram is still
the best image to evaluate these lesions since they are highly mobile
and can be better seen in high resolution mode or zoom mode.
Larger lesions may be accompanied by calcifications, which makes
it easier to identify them [1,5]. The differential imaging diagnoses
of this type of tumors include Lambal’s excrescences, which look
more linear and are smaller, the vegetations that are usually
accompanied by valve incompetence and destruction of the valve
leaflets, thrombi and valve degenerative changes. Although these
tumors are formed in the heart valves, the dysfunction of these
structures is rare [5,8,10]. Treatment of benign primary tumors
such as papillary fibroelastoma is surgical. Some authors suggest
that, in the case of tumors on the left side, they should be resected
in patients without high surgical risk if the size is greater than 1
cm or during another type of heart surgery. In the case of lesions
on right side of the heart, they should only be resected if they are
large or moving, and if they are associated with a hemodynamically
significant obstruction or with a high risk of embolism due to short
circuit from right to left [5,14]. Although a significant percentage
of patients are asymptomatic, we suggest that those that meet
the aforementioned criteria be resected, given the high risk of
cerebrovascular events and death, aiming to use a technique that
conserves the native valve [1,15]. If the patient does not have
any symptoms or if the tumor is small, has no pedicle and is not
moving, of if it is not possible to perform the surgical procedure
due high surgical risk or due to the patient’s preference, we suggest
antiplatelet therapy, even though there are few publications that
support this recommendation [5,15].
Conclusion
Primary cardiac fibroelastoma of the papillary fibroelastoma
type are rare masses that are usually found incidentally during
routine exams conducted to frequently asymptomatic patients.
The image that can best characterize this type of mass is the
transesophageal echocardiogram and the recommended
management is surgery, considering the risk of embolic events and
the individual characteristics of both the patient and the tumor,
Ethical Responsibilities
Protection of people and animals. The authors declare that no
experiments have been conducted on humans or animals for this
research.
a. Data Confidentiality: The authors declare that they have
followed the protocols of their work center on the publication
of patient data. Right to privacy and informed consent. The
authors declare that patient data does not appear in this paper.
To Read More Please Click on below link
For more LupinePublishers Open Access Journals Please visit our website: https://lupinepublishersgroup.com/