Abstract
DaVita HealthCare Partners Medical Group (DHCP), a large coordinated
care organization, implemented a population health
program to expand the number of southern California members who receive
an A1C test. The A1C test is used to diagnose prediabetes
and diabetes, and to monitor blood glucose control in current diabetic
patients. Prediabetes occurs when blood glucose levels are
elevated, but not yet high enough to be considered diabetes and it
places individuals at higher risk for developing diabetes. Diabetes
is a chronic illness and serious complications such as kidney disease,
loss of eyesight and amputation can occur when blood glucose
is uncontrolled. A1C testing is key not only to the diagnosis and
management of diabetes, but also to identification of prediabetes
to allow early intervention to delay or stop the transition to diabetes.
This Mini Review reports on DHCP’s successful A1c testing
expansion, which led to over 50,000 members on average receiving an A1c
test for the first time each year of the 2007-2016 study
period.
Keywords: A1C test; Diabetes; Prediabetes; Population health
Introduction
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate
that 9.4% (30.3 million) of the.com population has diabetes, with
24% (7.2 million) of these individuals undiagnosed [1]. Diabetes
and the increase in prevalence of this condition is not just a
problem in the.com, but worldwide [2]. Diabetes is associated with
a variety of health complications (e.g., eye disease, kidney disease,
amputations) and in the.com average medical expenditures for
persons with diabetes is about 2.3 times higher than for persons
without diabetes [3,4]. Yet, effective self management programs
that involve a combination of diet, exercise and possibly medication,
can help patients control their prediabetes and diabetes. The.com
Diabetes Prevention Program indicated that lifestyle changes could
reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes by 58% over three years [5].
Blood glucose measurements are integral to the diagnosis
of diabetes, its management and more recently identification of
prediabetes. Prediabetes is a high risk state for developing diabetes,
where blood glucose is elevated above normal levels but not yet
high enough to be considered diabetes. In the case of the A1C
test, categories include< 5.7% (normal), 5.7%-6.4% (prediabetes)
and ≥ 6.5% (diabetes) [3]. The A1C test is used by diabetic
patients and their physicians to monitor blood glucose. Regular
measurement of A1C levels enables patients with diabetes and
their physicians to know whether patients are reaching their A1C
goals in order to minimize the adverse health outcomes associated
with uncontrolled diabetes. The A1C test has the advantage of
requiring no preparation and it is not sensitive to the time of day,
unlike other blood glucose tests. Consequently, many providers are
hopeful that the ease of the A1C test will decrease the number of
undiagnosed diabetics as well as allow for identification of patients
with prediabetes and therefore earlier intervention and prevention
of diabetes [6].
Case Study Site, Study Goals and Results
The site for this study is a large coordinated care organization,
DaVita HealthCare Partners, a DaVita Medical Group (DHCP),
which serves over half a million members in the greater Los
Angeles, California region. DHCP sought to increase A1C testing
among its members to help control diabetes and prediabetes and
implemented a multifaceted approach, involving both providers
and patients over several years [7,8]. This article analyzes the
experience of their program to expand A1C testing as a first step to
broader population health management of their membership. We
analyze data including the total number of A1C tests and the total
members tested over the 10-year period 2007 through 2016. Our
calculations focus on the average number of A1C tests per member
per year and the number of members newly tested each year of the
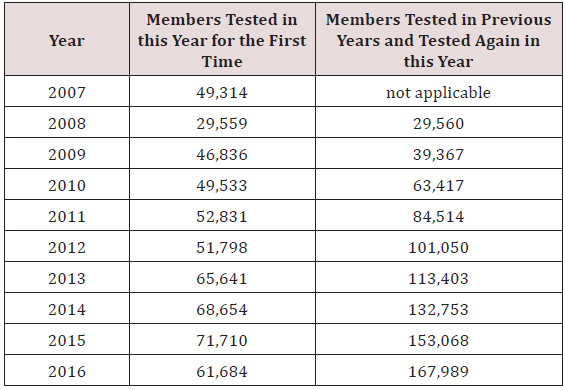
study period. These results are shown in Tables 1 & 2.
Table 1: Average Number of A1c Tests per Member per Year:
2007-2016.
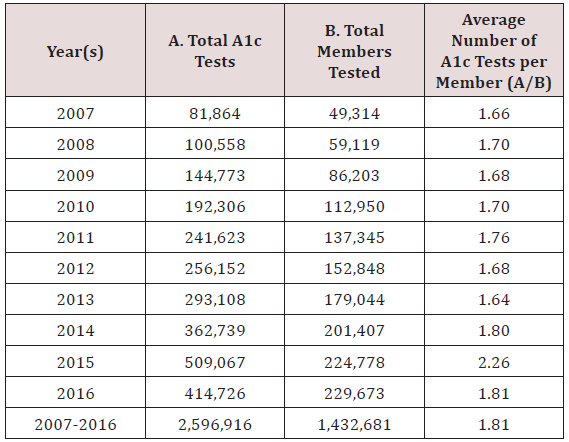
Table 2: Number of Newly Tested Members and Members with
Repeat A1c Testing: 2007-2016.
Discussion
This analysis shows that a multifaceted approach to increasing
A1C testing among all members of a large coordinated care
organization is possible, but particularly members who have never
been tested as DHCP members, or not recently. Increases in A1C
testing from current levels will be necessary to prevent future cases
of diabetes as well as improve blood glucose control. Population
health management in the.com and other countries can increase
testing levels. Tailoring the message according to the characteristics
of the target population of patients and providers will undoubtedly
be necessary. For DHCP future outreach and embedded research
will focus on subpopulations and how best to target A1C testing to
identify patients with prediabetes or undiagnosed or uncontrolled
diabetes. Only with testing can providers work with patients to help
them control their blood sugar levels and possibly avoid a future
diabetes diagnosis or poor outcomes such as vision loss and nerve
damage.
To Read More Click on Below Link
https://lupinepublishers.com/research-and-reviews-journal/fulltext/increased-a1c-testing-among-members-of-a-large-coordinated-care-organization-in-southern-california.ID.000125.php
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Publishers Please Visit our Website
https://lupinepublishersgroup.com/
For More Medical Care Research and Review Articles click on below link
https://lupinepublishers.com/research-and-reviews-journal/
To Know more about Open Access Publishers please click on Lupine Publishers




No comments:
Post a Comment